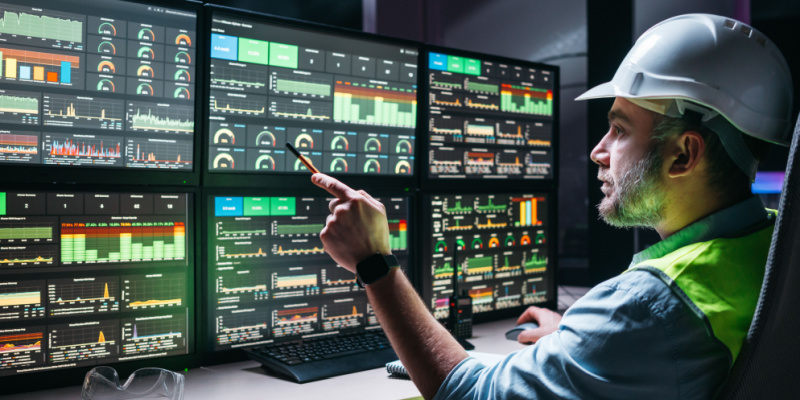
SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition. It is a system used in manufacturing and various industrial operations for monitoring and controlling processes. Here’s a breakdown of what SCADA entails:
- Supervisory Control: SCADA systems enable managers and operators to supervise entire manufacturing processes from a central location. They provide control over machinery and equipment, allowing adjustments to be made in real-time to optimize performance.
- Data Acquisition: These systems collect data from sensors and equipment across the manufacturing floor. This data includes temperatures, pressures, levels, flow rates, and other critical parameters.
- Monitoring: SCADA systems continuously monitor the state of the manufacturing equipment and processes. The interface usually displays this information in real-time, providing operators with visual representations such as graphs, charts, and alarm notifications for any anomalies.
- Automation: SCADA systems can automate repetitive tasks by following predefined instructions. This reduces the need for manual intervention, decreases the chances of human error, and increases efficiency.
- Data Logging and Analysis: They store historical data, which can be analyzed to identify trends, optimize processes, and improve decision-making. The information logged can be critical for maintenance planning, troubleshooting, and compliance with regulatory standards.
- Communication: SCADA systems typically consist of hardware components, including Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), that communicate with software in a central control room. This communication is crucial for the real-time monitoring and control of manufacturing operations.